It can be distressing when your child is diagnosed with a condition like aplastic anemia. Wondering how this will affect your child’s life and health on a long-term basis can be a source of stress and anxiety — and come with many questions. While aplastic anemia is a very serious illness, it is treatable, and many children are able to recover and return to a healthy and active life.
We’re happy to share the following informative overview to help you better understand this condition, the treatment options, and the care needs for your child. Informing yourself as a caregiver and parent of a patient will enable you to become more engaged with your treatment journey and achieve the best possible outcome for your family.
What is aplastic anemia?
Aplastic anemia is a medical condition that occurs whenever the body stops producing enough blood cells for healthy functioning. This makes people who are affected vulnerable to frequent and uncontrollable bleeding, as well as an increased risk of infection. Because blood cells of all types play such an important role in transporting oxygen, removing waste, and keeping up the body’s immunity, a lack of blood cells can have a negative impact on health.
The term aplastic, or aplasia, refers to an inability of the body to produce new tissue. Anemia refers to a lack of healthy blood cells and is most commonly associated with a lack of red blood cells. Aplastic anemia is related to bone marrow failure that can cause the body to be unable to produce healthy blood cells, including red cells, white cells, and platelets.
Aplastic Anemia Causes
Aplastic anemia can have a wide range of causes and affect people of all ages, including children. Most commonly, this condition develops when the body’s own immune system attacks stem cells in the bone marrow which normally produce blood cells.
Aplastic Anemia Risk Factors
Other contributing causes and risk factors can include genetics, chemotherapy or cancer treatment, exposure to toxins, other illnesses such as hepatitis or Epstein-Barr, and drug interactions. In some cases, doctors are unable to identify the underlying cause of aplastic anemia.
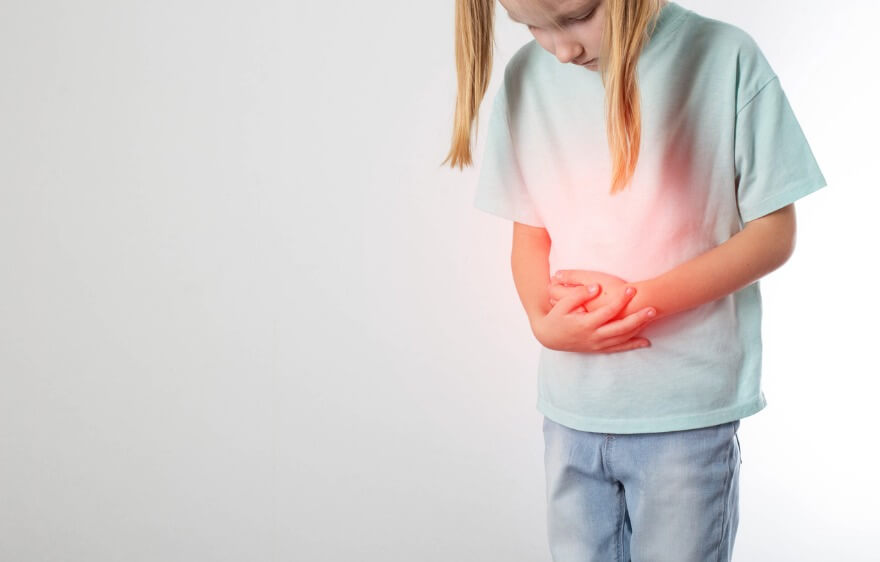
Aplastic Anemia Symptoms in Children
The condition can develop slowly with little or no symptoms, or it may come on suddenly. The most commonly experienced symptoms of aplastic anemia in children are:
- Acute tiredness and general fatigue
- Frequent bruising
- Prolonged bleeding when cut
- Nosebleeds and bleeding in the gums
- Headaches
- Shortness of breath or heavy breathing
- Pale skin
- High rates of infection
- Fever
- Dizziness
Aplastic Anemia Complications
Long-term complications also vary but can include the risk of heart disease, heart arrhythmia, heart failure, blood disease, cancer, and developmental delays.
Because aplastic anemia can have a range of severity and duration, it’s important to work closely with your doctor to ensure your child receives the best possible care.
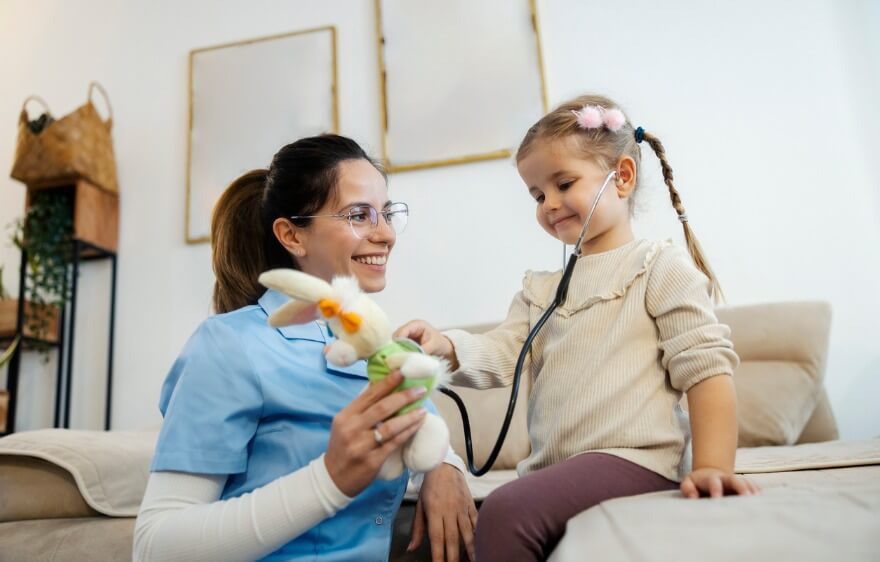
Diagnosing Aplastic Anemia
After a physical examination, questions about symptoms, and a review of medical history, a number of specific tests can typically confirm the diagnosis of aplastic anemia. The most common is blood work to determine if cell counts are outside of healthy parameters, and a bone marrow biopsy to measure cell levels and rule out other causes.
Pediatric Aplastic Anemia Treatment
Aplastic anemia in children is a highly treatable condition. The specific methods will depend on the severity of the condition and the patient’s age.
Treatment plans may include the following therapies:
- Blood transfusion of red blood cells and/or platelets by intravenous (IV) line
- Stem cell transplant, also called a bone marrow transplant, can help the body make more blood cells
- Medication, such as immunosuppressants, bone marrow stimulants, and antiviral drugs
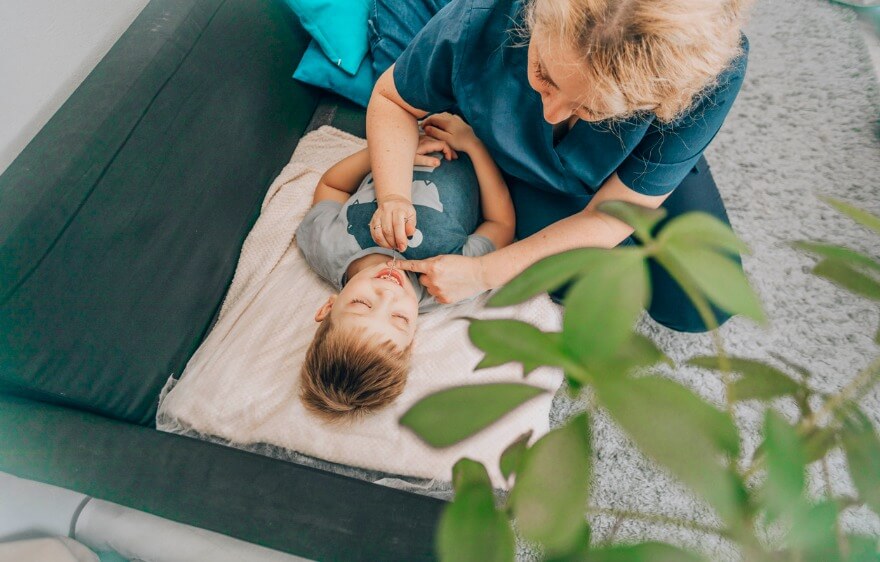
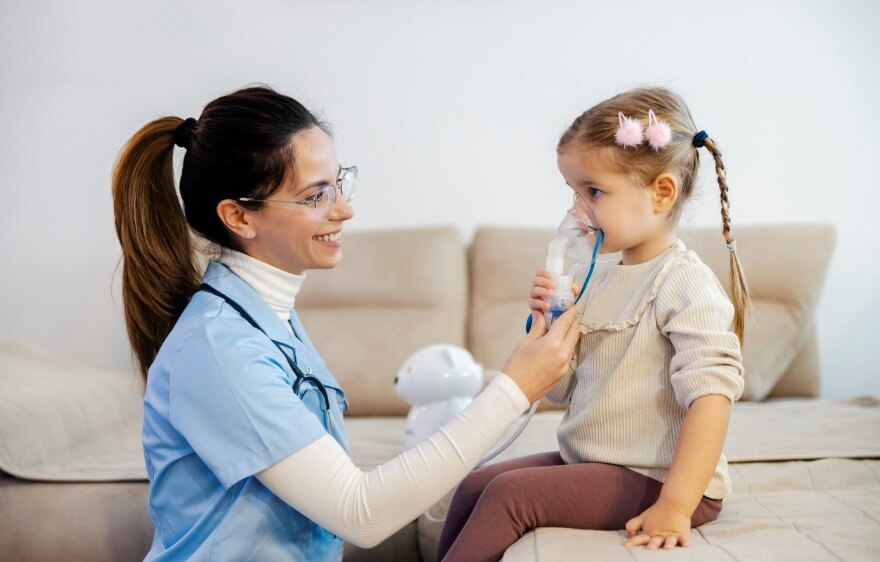
Caring for a Child with Aplastic Anemia
Children with aplastic anemia often have long-term care needs, including hospitalizations, frequent specialist appointments, increased home safety measures, and medication management. It’s important to monitor for signs of the condition and children with aplastic anemia are often advised to avoid contact sports and limit contact with sick or infected people.
In a large number of cases, families with busy schedules or limited caregivers benefit from the support of pediatric home health. Services can include supervision to provide a safe environment, accompanying your child to appointments, and assisting with nutrition and medication. Pediatric home health services can be a major asset to your child and family.
Contact Care Options for Kids for Home Health Care in Florida
It can be hard to balance your time between work, home, and caring for a child. That’s why our team of professionals at Care Options for Kids is here to help. We have been enforcing precautionary measures and following the Centers For Disease Control (CDC) guidelines for COVID-19 to ensure the safety and health of our clients and employees.
Our home health care services offer support in the comfort of your home. We refer loving and competent nurses to provide customized care for families — from a few hours a day to around-the-clock supervision. Contact us directly to speak with a home health care professional or request a free in-home assessment. Together we can determine the best plan of action to keep your loved ones happy and healthy.
If you or a loved one are considering Pediatric Home Health Care Services in Florida, contact the caring staff at Care Options for Kids. Call today at (888) 592-5855.