Finding out your child or loved one is dealing with a genetic disorder like neurofibromatosis is never easy. This news almost always comes with a list of questions and anxiety about what the future holds. From managing symptoms in the short term to meeting care needs to ensure healthy development, it’s hard to know what the future will hold.
We’re sharing the following guide to help you gain peace of mind and take charge of your little one’s care picture. By learning more about neurofibromatosis, including the causes, treatments, and long-term prognosis, you can make informed choices that enable the best possible outcomes for your family.
What is Neurofibromatosis?
Neurofibromatosis describes a rare group of genetic disorders that cause the development of tumors on nervous tissue throughout the body. While these growths are usually non cancerous, or benign, in some cases they can lead to cancer and other complications.
Neurofibromatosis Causes
Neurofibromatosis is caused by a genetic defect that can either be passed on through chromosomes or develop spontaneously during early growth. These defects disrupt proteins responsible for regulating cell growth and suppressing tumors. With neurofibromatosis, these proteins specifically affect nerve tissue.
The specific chromosome that causes neurofibromatosis depends on the type. NF1 is caused by a gene on chromosome 17 that disrupts the production of neurofibromin which helps regulate cell growth. The gene for NF2 is the 22nd chromosome and causes a loss of the protein merlin and an increased risk of tumors. Schwannomatosis is caused by mutations in the SMARCB1 and LZTR1 genes, which also help to suppress tumors.
Neurofibromatosis Risk Factors
Because it is a genetic condition, the single biggest risk factor for any type of neurofibromatosis is a family history of the condition. Children of parents with NF1 and NF2 have a 50% chance of inheriting the condition.
Neurofibromatosis Symptoms
Symptoms for neurofibromatosis also vary by type and can include:
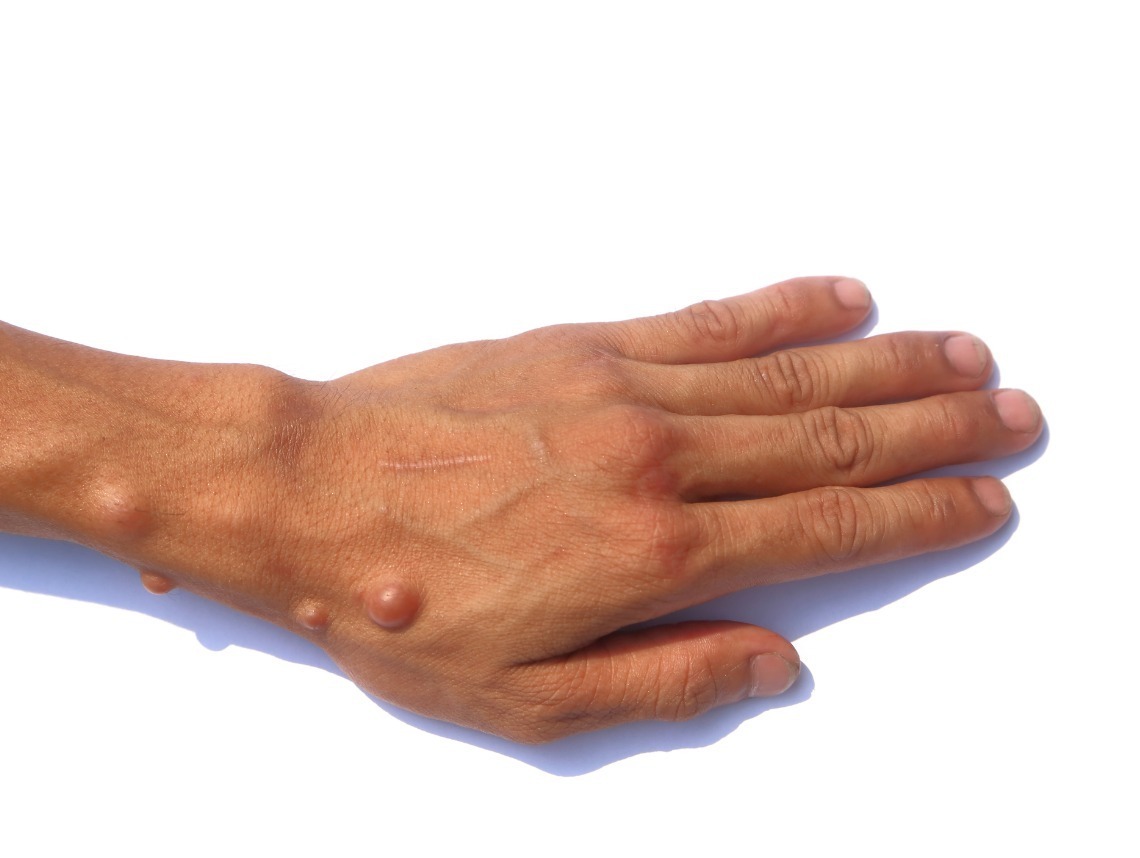
- Harmless, light brown spots on the skin, called cafe-au-lait spots
- Bumps under the skin, called neurofibromas
- Freckling
- Bone deformities
- Learning disabilities
- Slower, delayed, and inhibited growth
- Larger head sizes
- Gradual hearing loss, poor balance, headaches, and ringing in the ears for people with NF2
- Chronic pain, numbness, and loss of muscle, for patients with Schwannomatosis
Types of Neurofibromatosis
There are three main types of neurofibromatosis:
- Type 1: Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) is the most common type and is usually diagnosed in children under the age of 10. The signs and symptoms are usually relatively mild and noticeable immediately at birth or in the early months.
- Type 2: Neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) is a rarer type, affecting teens and young adults most often. In this type, neurological tumors affect the ears and vestibular system, causing hearing issues and balance problems.
- Schwannomatosis: This is the most uncommon form and typically affects people over the age of 20. Schwannomatosis can affect cranial and spinal nerves and cause debilitating pain, and neurological symptoms such as numbness and weakness.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of neurofibromatosis can help to diagnose this condition and treat it as early as possible and take action.
Neurofibromatosis Complications
Complications can vary and, in most cases, neurofibromatosis is mild and requires minimal treatment and management. In more serious situations, the condition can lead to neurological problems, skeletal deformities, and the potential for cancerous growths. This is why it is important to work closely with a doctor from the outset to ensure the best possible long-term care.
Diagnosing Neurofibromatosis
In most cases, doctors can identify NF1 early in life or at birth by certain visual signs and symptoms. In some cases, a physical examination, diagnostic testing, and genetic testing can help to further confirm the diagnosis. NF2 often requires additional testing, including balance tests, and hearing examinations to diagnose the condition.
Neurofibromatosis Treatment
Treatment can range from monitoring for the appearance of new skin abnormalities to an evaluation of growth and development to medications. In rare cases, surgery may be required to remove cancerous tissue or place auditory implants if the condition is affecting hearing.
Caring for a Child with Neurofibromatosis
Children with neurofibromatosis may require ongoing physical therapy to help with developmental delays, emotional and behavioral counseling to help adjust to the challenges of this condition, and nutritional needs in some cases.
Many families also turn to the support that pediatric home health services can bring. From respite care, to nutritional support, to accompanying children to appointments, a caring pediatric home health professional can help with a full spectrum of care needs.
Contact Care Options for Kids for Home Health Care in Florida
It can be hard to balance your time between work, home, and caring for a child. That’s why our team of professionals at Care Options for Kids is here to help. We have been enforcing precautionary measures and following the Centers For Disease Control (CDC) guidelines for COVID-19 to ensure the safety and health of our clients and employees.
Our home health care services offer support in the comfort of your home. We refer loving and competent nurses to provide customized care for families — from a few hours a day to around-the-clock supervision. Contact us directly to speak with a home health care professional or request a free in-home assessment. Together we can determine the best plan of action to keep your loved ones happy and healthy.
If you or a loved one are considering Pediatric Home Health Care Services in Florida, contact the caring staff at Care Options for Kids. Call today at (888) 592-5855.