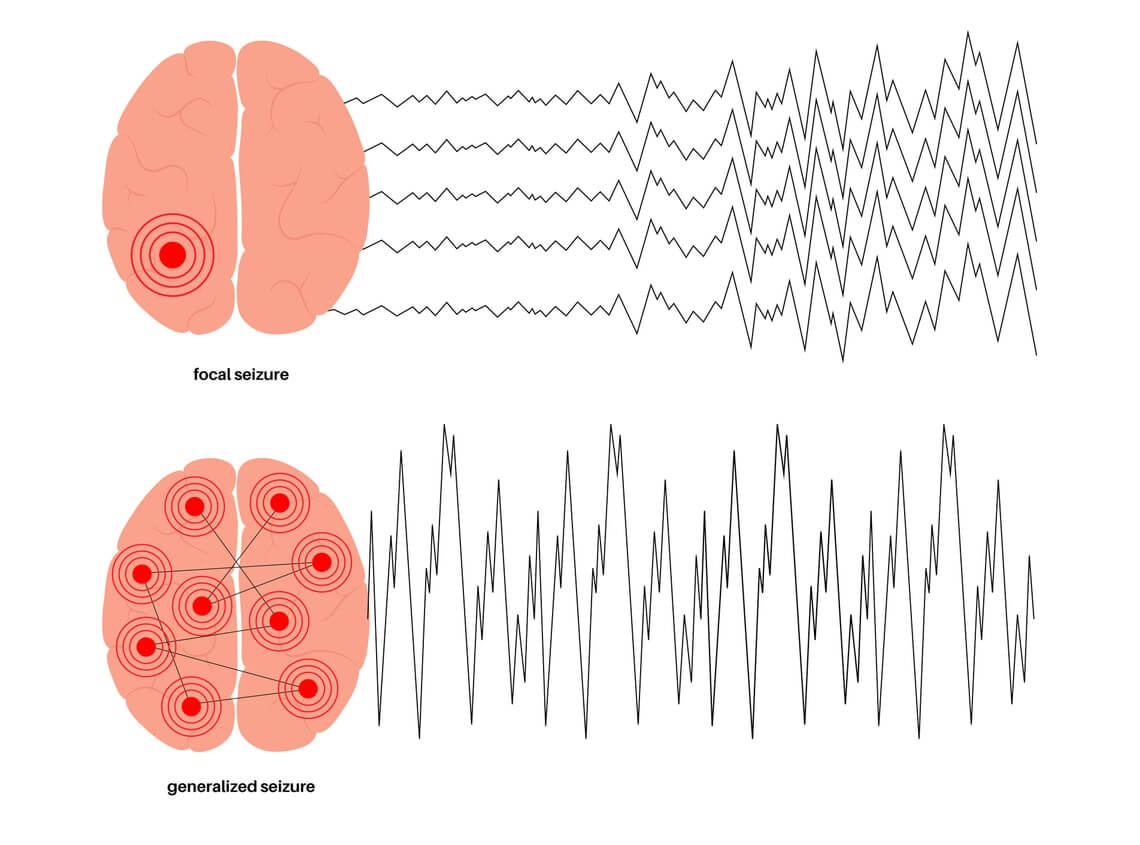
Although the many different types of seizures can be confusing and a little overwhelming, learning the basics is an important step. According to the Epilepsy Foundation, there are two main types of seizures: focal seizures and generalized seizures.
The main difference between these two seizure types is where they begin in the brain.
Basically, a focal seizure begins in one area of the brain while a generalized seizure encompasses the entire brain. These types of seizure terms are related to the “onset” of the seizure, or where and how the seizure originates. Knowing where the onset of a seizure occurs can tell doctors important things about likely symptoms and effects of seizure episodes.
The following guide will give you a deeper understanding of focal and generalized seizures, including treatment options and care needs if your child or loved one is dealing with either of these events. By educating yourself as a parent, you can become more engaged and confident with your little one’s care needs.
What is a Focal Seizure?
Also called focal onset seizures, and formerly known as partial seizures, focal seizures start in one specific area or side of the brain. Focal seizures are further divided into focal aware and focal impaired awareness seizures:
- Focal aware seizure: Also known as a simple partial seizure, the person remains awake and aware during the event. The person may appear frozen for a brief period of time, and many report experiences such as phantom scents and deja vu.
- Focal impaired awareness seizure: This is when the person loses awareness during the event. Common symptoms include lip smacking, picking at clothing, and wandering.
Focal seizures can potentially develop into generalized seizures, which is known as a secondary generalized seizure.
What is a Generalized Seizure?
Generalized seizures start on both sides of the brain. There are a large number of sub-types of generalized seizures related to the level of awareness and the type and intensity of related movements. The two most commonly known types of generalized seizures include:
- Absence seizures: Under older terminology, this was known as a “petit mal” seizure. These very brief seizures usually involve blanking out or staring off into space, often accompanied by blinking or fluttering eyes.
- Tonic-clonic seizures: Formerly called “grand mal” seizures. These are two-phase general onset seizures, with a tonic phase that involves stiffening and a clonic phase that involves rhythmic jerking.
There are other types of generalized seizures, including separate tonic seizures and clonic seizures, atonic seizures, and myoclonic seizures. Despite the fact that generalized seizures encompass the entire brain, this type of onset can still result in a wide range of specific symptoms and manifestations.
What are the similarities and differences between focal and generalized seizures?
Any type of seizure is caused by a disruption in the normal electrical activity in the brain, which is also called a discharge. Both generalized and focal seizures will also generally happen in three distinct phases that are common among seizures:
- The prodrome, or middle, phase — also sometimes called an aura — which can be marked by slight changes in mood.
- The ictal phase, which is the primary part of the seizure characterized by intense electrical activities and pronounced symptoms.
- The postictal phase, which is when the seizure has subsided and the body and mind recover. People often report tiredness, confusion, and slight nausea after both generalized and focal seizures.
As discussed above, the main difference between focal and generalized seizures is where they originate in the brain. While there are differences between symptoms for the sub-types, the fact is that seizures can vary so widely on a case-by-case basis, that it is difficult to list basic symptoms as related to generalized or focal onset seizures.
If your child or other loved one is experiencing any type of seizure or has developed new symptoms, it is important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosing Focal and Generalized Seizures
For both focal and generalized onset seizures, doctors will usually perform a similar evaluation to diagnose and treat these episodes. Diagnostic steps can include:
- Physical examination
- Detailed questions about the seizures and potential triggers
- Review of medical history
- Tests, including an electroencephalogram (EEG) or magnetic resonance imagery (MRI) to detect abnormal brain waves or structures in the brain
Additionally, a video recording of the event can be very helpful in diagnosing the type of seizure a patient is having.
Focal and Generalized Seizure Treatment
Generalized and focal onset seizures are often treated with similar methods upon diagnosis as well. Anticonvulsant medications are often prescribed for both types, as well as recommendations for nutritional adjustments, such as a higher-fat ketogenic diet.
Caring for a Child with Focal and Generalized Seizures
Both of these seizure types can also come with complex and dedicated care needs for children. Many families rely on pediatric home health services for a wide range of support, including providing a safe environment, helping with nutrition, and assisting with medication.
Contact Care Options for Kids for Home Health Care
It can be hard to balance your time between work, home, and caring for a child. That’s why our team of skilled professionals at Care Options for Kids is here to help. We have been enforcing precautionary measures and following the Centers For Disease Control (CDC) guidelines for COVID-19 to ensure the safety and health of our clients and employees.
Our home health care services offer support in the comfort of your home. We refer loving and competent nurses to provide customized care for families — from a few hours a day to around-the-clock supervision. Contact us directly to speak with a home health care professional or request a free in-home assessment. Together we can determine the best plan of action to keep your loved ones happy and healthy.
If you or a loved one are considering Pediatric Home Health Care Services, contact the caring staff at Care Options for Kids. Call today at (888) 592-5855.